Contents
An examination of global warming explains its causes, including the greenhouse effect from human activity, the devastating consequences of global warming, and the actions needed to prevent global warming.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the long-term, sustained increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s climate system. This phenomenon is a primary aspect of current climate change and has been confirmed by direct temperature measurements and various other observations. The scientific consensus is clear: the Earth’s climate is warming at an unprecedented rate, and this trend of global warming is almost certainly driven by human activity. Understanding what is global warming is the first step toward addressing its profound impacts. The record of global warming is alarming, highlighting a critical need for action to mitigate further temperature rises.
The Greenhouse Effect Explained
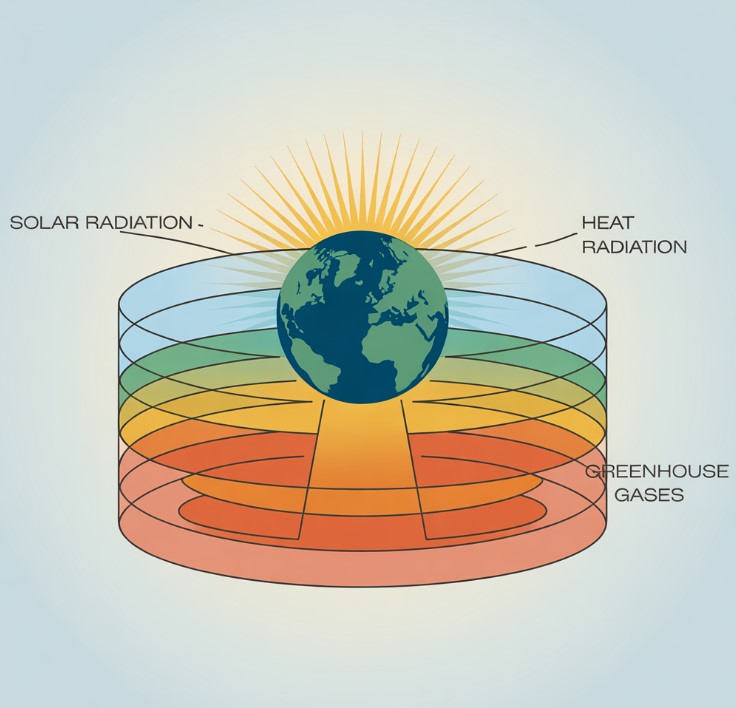
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space, and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases include:
- Water vapor
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
- Methane (CH₄)
- Nitrous oxide (N₂O)
- Ozone (O₃)
This natural effect is essential for life, as it keeps our planet warm enough to sustain it. However, increased concentrations of greenhouse gases from human activity have enhanced the greenhouse effect, trapping more heat and causing global warming.
What are the Two Hypotheses of Global Warming?
While the scientific consensus points overwhelmingly to human activity, it is useful to understand the primary hypotheses discussed regarding the causes of global warming.
| Hypothesis | Description | Scientific Consensus |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Cycles | This hypothesis suggests that current global warming is primarily a result of natural fluctuations in the Earth’s climate, such as volcanic activity or variations in solar radiation and glacial cycles. | Not supported by the vast majority of climate scientists. While natural cycles do influence climate, they do not account for the rapid rate of warming observed since the mid-20th century. |
| Human Activity | This hypothesis, backed by overwhelming evidence, states that human activity is the main driver of current global warming. The relationship between industrial revolution and global warming is central to this theory. | The most widely accepted scientific explanation. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has concluded that it is “unequivocal” that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This is the core issue of global warming. |
The evidence strongly supports the second hypothesis, linking the surge in global warming to the start of the Industrial Revolution, when humans began burning fossil fuels on a massive scale.
Causes of Global Warming
The primary causes of global warming are rooted in human activity that increases the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: The combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy and transportation is the largest source of carbon dioxide emissions, a potent greenhouse gas driving global warming.
- Deforestation: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere. Clearing forests for agriculture, logging, and development reduces this capacity, contributing to global warming.
- Industrial Processes: Many industrial activities release powerful greenhouse gases, including fluorinated gases. Cement production alone is a significant source of CO₂.
- Agriculture: Agricultural practices, particularly livestock farming, release large amounts of methane. Fertilizers used in farming also release nitrous oxide. These activities are significant contributors to the problem of global warming.
Consequences of Global Warming
The effects of climate change on the planet due to global warming are far-reaching and severe. These consequences of global warming impact ecosystems, economies, and human societies.
Melting of the Poles
One of the most visible consequences of global warming is the rapid melting of the poles and glaciers. This contributes directly to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems worldwide. The melting of the poles also disrupts habitats for species like polar bears.
Extreme Weather Events
Global warming intensifies weather patterns. The question of how does global warming cause extreme weather events is answered by the increased energy in the climate system. Warmer ocean waters fuel more powerful hurricanes, while changes in atmospheric circulation lead to more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, floods, and wildfires. This is a direct consequence of global warming.
Ocean Acidification
The oceans absorb about a quarter of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from human activity. This process causes the water to become more acidic, harming marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells like corals, shellfish, and plankton. This is one of the less visible but equally damaging consequences of global warming.
Loss of Biodiversity
Rapid climate change alters habitats faster than many species can adapt. This leads to shifts in ecological niches and, in many cases, extinction. The threat to biodiversity is a serious consequence of unchecked global warming.
Impacts on Agriculture and Food Security
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns disrupt food production. Some regions face crop failures due to drought, while others experience losses from flooding. This poses a significant risk to global food security, a direct result of ongoing global warming.
How to Avoid and Prevent Global Warming
Addressing the challenge of global warming requires a coordinated global effort. The primary goal is reducing the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere. Here is how to avoid and prevent global warming through collective and individual actions.
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power is the most critical step to prevent global warming. This reduces the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions causing global warming.
- Improve Energy Efficiency: Consuming less energy in homes, businesses, and transportation reduces the demand for fossil fuels. This includes using energy-efficient appliances, improving building insulation, and adopting sustainable transportation methods.
- Promote Reforestation and Sustainable Land Use: Protecting existing forests and planting new trees helps absorb atmospheric CO₂. Sustainable agriculture and land management practices can also reduce emissions and improve soil health, which helps to prevent global warming.
- Implement Government Policies: Governments can enact policies such as carbon pricing, emissions standards for industries and vehicles, and investments in green technology. International agreements are essential for coordinating a global response to global warming.
- Individual Actions: Individuals can contribute by reducing their carbon footprint through choices in diet, transportation, and consumption. Supporting businesses and policies committed to sustainability is another way to help prevent global warming.
FAQ on Global Warming and Climate Change
Q: Is global warming the same as climate change?
A: Global warming refers specifically to the sustained increase in the average temperature of the Earth. Climate change is a broader term that includes global warming and its side effects, such as changes in precipitation, the melting of the poles, and the frequency of extreme weather events.
Q: Are the effects of climate change on the planet reversible?
A: Some effects of climate change, such as ocean acidification and species extinction, will take centuries or millennia to reverse. However, immediate and substantial action to prevent global warming by reducing the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere can limit the most catastrophic consequences of global warming and allow ecosystems to begin to recover.
Q: What is the most significant human activity causing global warming?
A: The most significant human activity causing global warming is the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas) for energy production and transportation. This single activity is responsible for the majority of carbon dioxide emissions, the primary greenhouse gas driving global warming.
Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) – Climate Change and Global Warming
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)





