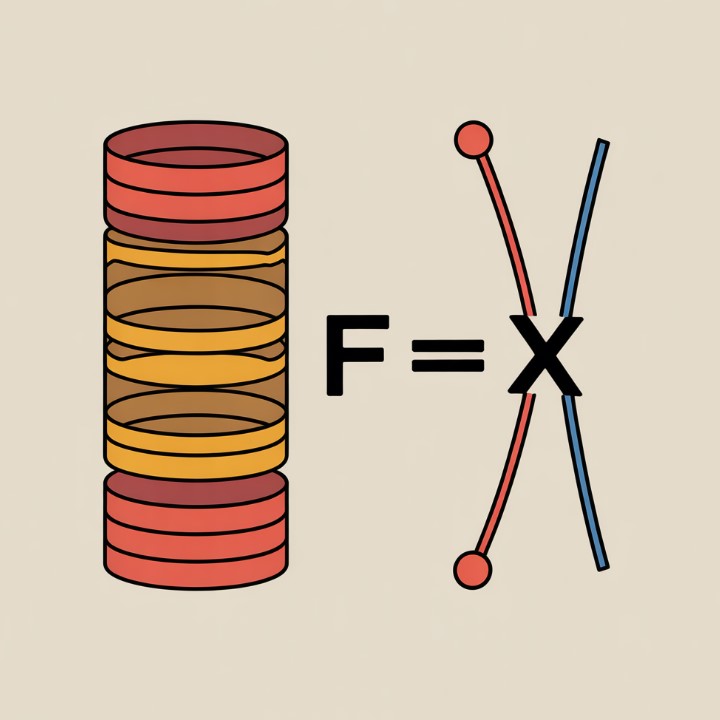Contents
Elasticity and elastic force are fundamental principles of physics that underpin countless aspects of our everyday lives, from the functioning of elastic materials like rubber bands to the operation of bungee cords, trampolines, and even our body organs.
What is Elasticity?
Elasticity is the property of a material to return to its original shape after being stretched, compressed, or deformed. It is directly associated with elastic force, which is the restorative force developed within a material when an external force deforms it. This resistance enables objects to recover their shape and maintain stability.
- Examples: Rubber bands, springs, and trampolines
How Elastic Force Works: Scientific Explanation
Elastic force follows a principle of proportionality, where the greater the force applied to stretch or compress an elastic material, the greater the restorative force pushing back. This is an application of Hooke’s Law, which can be mathematically summarized as:
F = -kxWhere:
- F is the elastic force,
- k is the elasticity constant of the material, and
- x is the amount of deformation (stretch/compression).
This force acts in the opposite direction to the applied force, creating a counterforce that restores the material’s original shape.
Real-Life Examples of Elastic Force:
- Rubber Bands
A rubber band stretches when pulled but returns to its original form upon release, showcasing how external force is resisted by elastic force. - Bungee Jumping
A bungee cord stretches under the jumper’s weight but prevents free fall by developing strong restorative forces. - Trampoline Design
When you jump on a trampoline, its surface stretches downward, and elastic force pushes you back up. - Body Organs – Elasticity in the Human Experience
Muscles and body tissues rely on elasticity for movements like breathing and digestion. For instance:
- Stomach walls stretch during eating but contract afterward.
- Arteries expand and contract for smooth blood flow.
- Springs and Mattresses
Springs in mattresses, and modern materials like memory foam, use elastic principles to provide comfort and support.
Elastic Materials in Everyday Life
Definition of Elastic Materials:
Elastic materials are substances that exhibit elasticity. These materials temporarily deform under stress and return to their original shape when the stress is removed.
| Material | Application | How Elastic Force Works |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber Bands | Hold objects together, organizational use | Counteracts stretching, returning to its looped shape |
| Resistance Bands | Fitness and muscle training | Produce resistance during stretching to help improve strength |
| Elastic Waistbands | Clothing, particularly for flexibility and movement | Expand to accommodate size while regaining the original fit |
| Springs | Mechanical devices, suspension systems | Store and release energy through compression/stretching cycles |
| Trampolines | Recreation and fitness | Absorb the jumper’s weight and bounce it back with an upward elastic force |
| Memory Foam/Spring Mattresses | Sleeping and furnishings | Conform to body shape and return to normal after use |
Elastic Force in Adventure Sports
Bungee Jumping:
A bungee cord’s elasticity ensures the jumper’s safety by slowing the descent and absorbing gravitational energy. The cord’s elastic force works as a counter to the pull of gravity, stabilizing the motion.
Trampolines:
Trampolines rely on elastic force for their bouncing effect. The fabric stretches under the jumper’s weight and uses elastic potential energy to push the user upward.
- This is an example of energy conservation, where mechanical energy is stored and recycled in elastic systems.
Elasticity in Musical Instruments
Elasticity is crucial in musical instruments like guitar strings. When plucked, the strings vibrate due to deformation of elastic materials, producing sound. The ability to deform and recover defines the pitch and tone.
- Deformation, Stretching, Elastic force.
- Deformation of guitar strings to produce sound.
Biological Examples of Elasticity
Applications in the Human Body:
1. Body Organs
Functioning body organs like the lungs and arteries use elastic fibers to expand and contract as needed. For example:
- Elasticity in Digestion: The stomach stretches to store food and contracts during digestion.
- Elastic Arteries: Help maintain consistent blood circulation, stretching during high pressure and contracting at low pressure.
2. Muscle Flexibility
Resistance bands work by leveraging elastic force to help muscles stretch and strengthen, mimicking the function of natural elasticity in tissues.
Fun and Functional Uses of Elastic Force
- In Entertainment
- Elastic springs create fun with toys, such as wind-up gadgets.
- In sports, bows and arrows function due to the elastic stretching of the bowstring.
- Household Items
- Springs used in modern mattresses provide comfort by resisting compression and adapting to body weight.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is an example of elastic force in daily life?
Common examples include stretching a rubber band, using a bungee cord, or jumping on a trampoline, where objects stretch under force but then return to their original shape.
Q2: How does elasticity work in the human body?
Body organs like lungs and arteries expand or contract due to the presence of elastic fibers, enabling essential processes like breathing and blood flow.
Q3: Why is elasticity important in engineering?
Elastic materials ensure structures can withstand forces (e.g., earthquakes or heavy loads) by absorbing stress and preventing permanent deformation.
Conclusion
Elasticity and its associated elastic force govern vital processes across physics, biology, and engineering. From bungee jumping to guitar vibrations, from elastic mattresses to muscle stretching, these phenomena demonstrate how versatile and essential elastic forces are in our daily lives. Whether for comfort, safety, or fun, elastic materials and principles continue to shape the modern world.