Contents
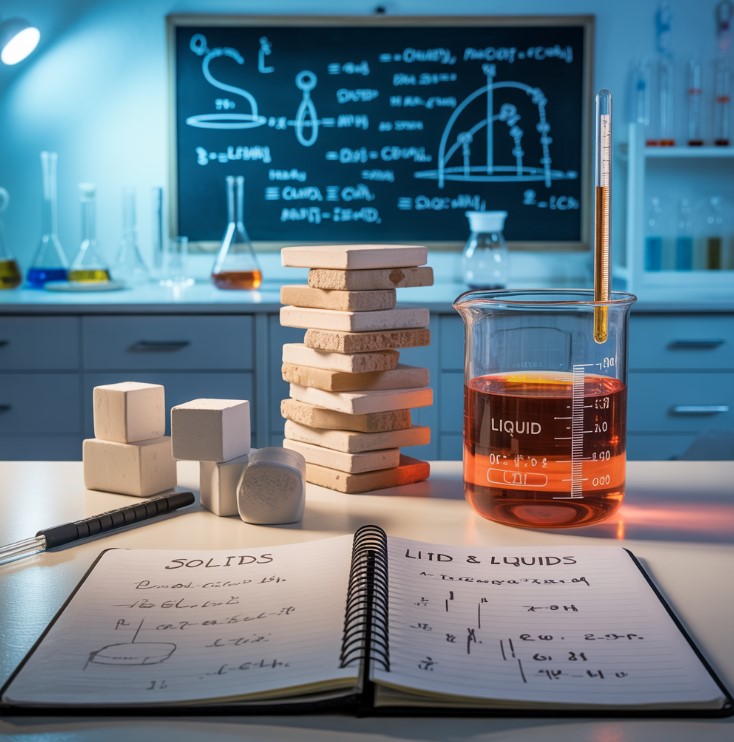
Hey! Let’s learn about solids & liquids – two common forms of stuff around us! They’re both types of matter (what everything is made of). Ready to dive in?
Think about making tea: When you heat ice (a solid) it turns into water (a liquid)! That’s a change because of temperature.
Examples:
- Ice: Hard, keeps its shape. Melts into water when it gets warm.
- Water: Flows, takes the shape of its container. Essential for life!
- Sand: Tiny bits of rock. Used for building & making glass.
- Mercury: A metal that’s liquid at room temp. Used in thermometers.
- Lead: A hard metal used in batteries & protection from harmful rays.
- Cooking Oil: Flows easily, used for cooking.
- Steel: Strong & hard, used for buildings & cars.
- Plastic: Can be hard or flow when heated. Used for tons of things!
- Milk: A liquid we drink for nutrients.
- Diamond: Super hard, used in jewelry.
(Basically, solids hold their shape, liquids don’t!)
More Examples (Lots!):
- Gasoline (liquid)
- Quicksand (mix of solid & liquid)
- Liquid Helium (super cold liquid)
- Aluminum (solid)
- Rubbing Alcohol (liquid)
- Chocolate (solid, usually!)
- Glass (solid)
- Ink (liquid)
- Copper (solid)
- Crude Oil (liquid)
- Wood (solid)
- Paint (liquid)
- Table Salt (solid)
- Orange Juice (liquid)
- Coal (solid)
- Motor Oil (liquid)
- Recycled Plastic (solid)
- Perfume (liquid)
- Silver (solid)
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) (liquid when very cold)
- Wet Beach Sand (mix of solid & liquid)
- Gold (solid)
- Vinegar (liquid)
- Paper (solid)
- Mud (mix of solid & liquid)
What are Solids & Liquids?
They’re two of the three main forms matter can take (the third is gas).
- Solids: Have a set shape & size.
- Liquids: Have a set size, but change shape to fit their container.
Key Differences:
Solids:
- Shape: Stays the same.
- Particles: Packed tightly together, neat & organized.
- Size: Doesn’t change.
Liquids:
- Shape: Changes to fit the container.
- Particles: Packed tightly, but move around & aren’t organized.
- Size: Doesn’t change.
Solid vs. Liquid – What’s the big deal?
It’s all about how the tiny bits inside are arranged! Solids are neat, liquids are more chaotic.
Important Properties:
Things like how heavy they are (density), if they dissolve in water (solubility), and how well they conduct heat (thermal conductivity) are important to know.
How do we measure how heavy something is for its size? (Density)
You divide the weight (mass) by the size (volume).
Temperature & Changes:
Heating a solid can turn it into a liquid (melting). The temperature where this happens is called the melting point.
Where are they used?
Everywhere! Building, making things, cooking, medicine… you name it!
In Everyday Life:
We use them all the time! Drinking water (liquid), walking on the ground (solid).
Real-World Example: Ice Cream!
Solid ingredients (sugar, fruit) are mixed with liquids (milk, cream) and then frozen to make ice cream.
A Little History:
People have been studying solids & liquids for a long time, but scientists like Galileo & Newton helped us understand them better.
Why are they important to science?
They help us understand how the world works and create new technologies.
Studying Solids & Liquids:
Scientists look at their properties and how they behave.
To Recap:
Solids have a set shape & size. Liquids have a set size but change shape.
Conclusion:
Solids & liquids are super important parts of our world and understanding them helps us understand everything around us!
Acronyms Used:
- Matter: The stuff everything is made of.
- LNG: Liquid Natural Gas
- GNL: Gas Natural Licuado (Spanish for LNG)
I hope this explanation is easy to understand! Let me know if you have any questions.